Physical explanation of the impossibility of the so called global warming effect!
1.Introduction
2.Misleading characterization
3.Contradiction to the first law of Thermodynamics
4.The 33 degree centigrade "mistake"
5.Contradiction to the second law of Thermodynamics
6.Interaction between radiation and so called greenhouse-molecules
7.Experimental disproof of the so called "green house effect"
1.Introduction:
The aim of this article is to deliver an explanation based on laws of physics of the impossibility of the alleged warming effect of "greenhouse gasses“ like CO2 or others.
This controversy is dealt with like a question of faith:
The opponents of this allegation refer to former natural climate changes, while the supporters of this allegation are convinced that the recent climate change is caused by human industrial activities.
This presentation shall be easily understood by a broader public and is therefore a little bit shortened. Therefore it is not a scientific treatise.
2. Misleading characterization
For about thirty years mainstream media Have been claiming the existence of so called "greenhouse gasses“ in the atmosphere , which allegedly reflect thermal radiation as it happens similar in a real greenhouse heating up the atmosphere in it.
Even this terminology was deliberately choosed, if the function of a real greenhouse is considered:
A real greenhouse is made of a glass body, which is transparent for visible radiation. This radiation is absorbed by the soil at the bottom of the greenhouse and re-emitted as thermal radiation, which heats up the air within the greenhouse. Without the glass body, the heated-up air would rise up by convection.
This is a regular process which eternally governs the weather activity:
Because of the declination of the incoming radiation with the latitude and the rotation of the earth, rotational air currents emerge.
These up-currents are used by birds and gliders . If those up-currents are hindered by a glass body, the air within this glass body heats up.
The so called "greenhouse gasses“ should have the same effect like the glass body of a real greenhouse, which is obviously impossible, because these gas molecules are part of the air and rising together with the other molecules of the air.
Even if the greenhouse molecules would be fixed in the air (what they are not), about 400 ppm CO2 would not be able to hinder all other molecules to rise.
This explanation of the warming effect of so called „greenhouse gasses“ is not only deliberately misleading, but contradicts fundamental laws of physics:
3. Contradiction to the first law of thermodynamics
(see first law of thermodynamics)
This law states the conservation of energy; energy can be transformed from one form to another, but can be neither created nor destroyed.
The so called „greenhouse effect“ contradicts this law for two reasons:
a) The internal energy of any body and especially of a gas depends on its temperature: for ideal gasses following formula is valid:
E=C*T
E denotes the internal energy, C the heat capacity of the gas and T the absolute temperature
(see Internal_energy).
That means: the internal energy of an ideal gas rises with the temperature. If the temperature of the atmosphere rises, its internal energy rises proportionally.
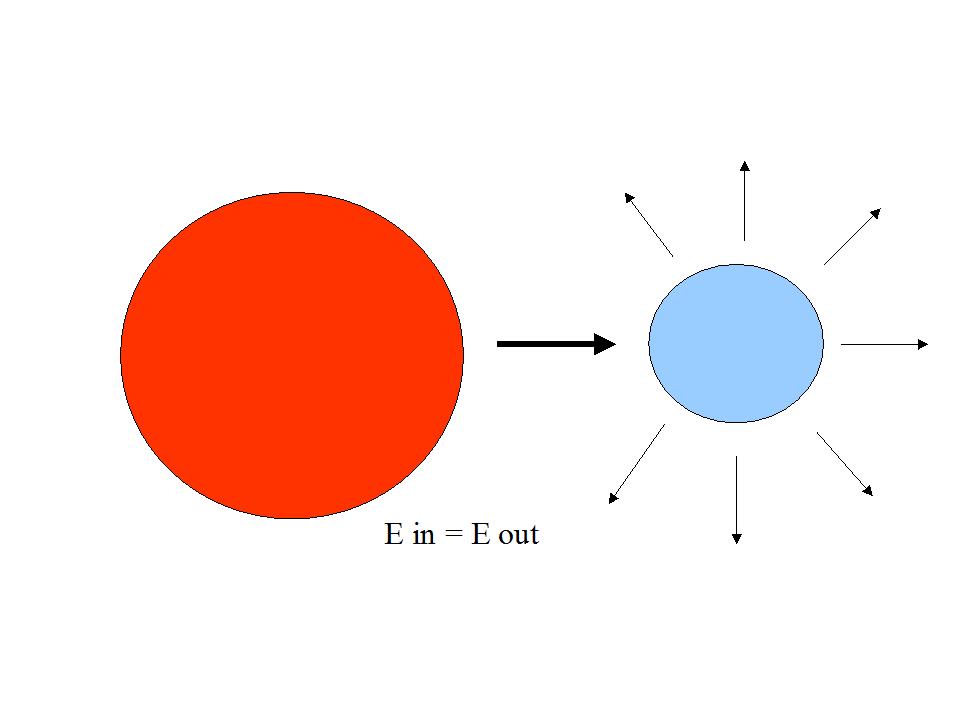
The question therefore is, where this additional energy comes from, as long as the earth is in a radiation equilibrium with the sun
(that means, that the earth emits the same amount of energy into the universe as it gets from the sun ).
 b) According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law of radiation the following formula is valid:
b) According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law of radiation the following formula is valid:
P=σ*A*T4
P denotes the radiated energy, σ the Stefan-Boltzmann-constant, A the area of the body and T the absolute temperature
It is important to understand that this formula is independent of the kind of body, its composition or kind of surface.
This formula is valid for an oven in the living room, as well as for the sun or a planet.
If the so-called "greenhouse gasses“ should cause a rise of the temperature of the atmosphere, the energy radiated from the earth has to rise according to this law, too:
Assuming that the temperature of the atmosphere rises by three degrees centigrade, which is about one percent of the absolute temperature of the air near the ground level,
the radiated energy has to rise by about four percent (1,014 is about 1,04)!
The question is therefore where this additional energy radiated by the earth should come from, as long as the earth and the sun is in a radiation equilibrium?
Are the "greenhouse gasses“ the source of that energy? The "greenhouse gasses“ would then be a new kind of perpetuum mobile!
4.The 33 degree centigrade "mistake"
It is interesting to realise that the popular scientific explanations of the global warming effect try to put the validity of the Stefan-Boltzmann-law into question:
This explanation goes as follows:
A kind of radiation balance is set up. Those parts of the incoming radiation which are directly reflected are deduced from the incoming radiation energy (albedo effect).
According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law a temperature is now calculated based on the reduced radiation energy. The result is about –18°C.
It is assumed that this calculation is valid up till now.
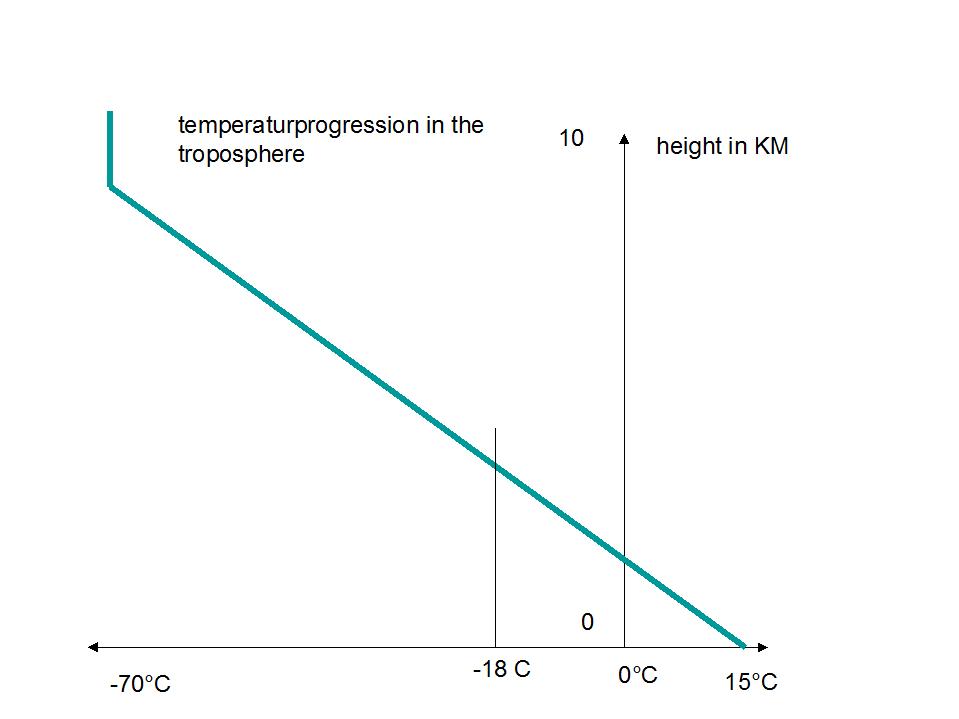
The trick of that deception is to interpret the result of –18°C as a temperature on ground level which is in reality about 15°C. Therefore a temperature gap of 33°C is ascertained.
It is asserted that this difference is the result of the greenhouse effect. Obviously this calculation yields a sort of average temperature of the whole troposphere, which varies from 15°C down to –70°C (tropopause)
(see Troposphere)
The calculated –18°C are therefore a reasonable average value.
In reality this difference is explained by the barometric formula (see Barometric formula )
and the gas law (see Gas laws).
As is well known the air pressure rises to the bottom because of the rising weight of the air column above and vice versa. Everybody knows that the air becomes dangerously thin in high altitude
(e.g. each year mountaineers are dying at the Himalaya because of the dangerous shortage of air)
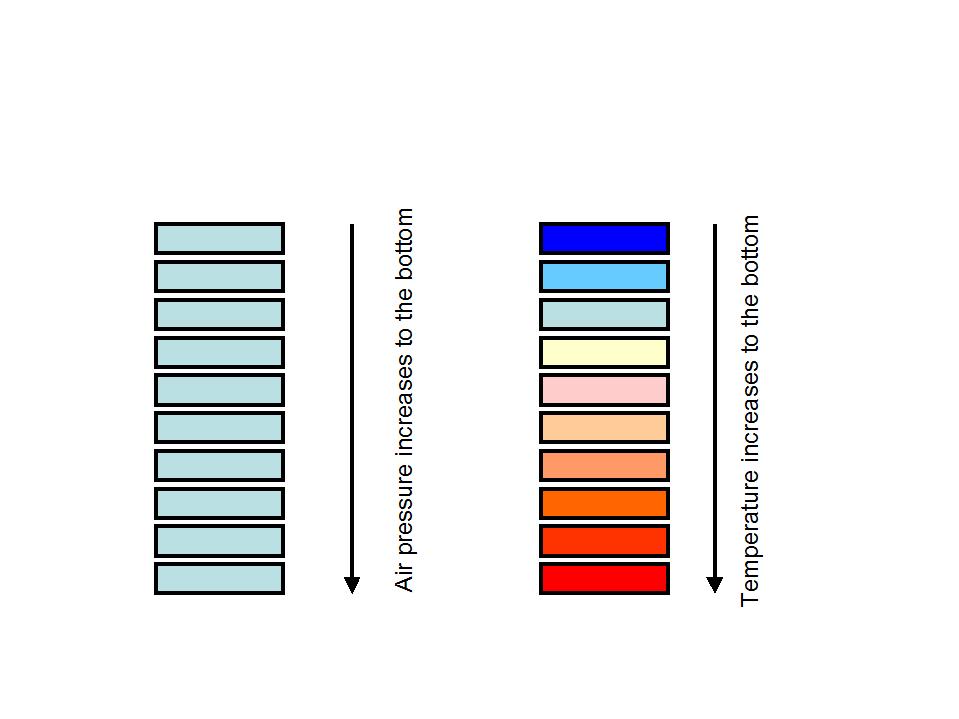
In combination with the gas law (see Gas laws)
P*V=R*T
(P air pressure, V volume, R the universal gas constant, T absolute temperature)
the declining air pressure yields a declining temperature with height.
Everybody who ever climbed on a mountain knows that the temperature in the height is lower than below.
The precise calculation of the so-called dry adiabatic lapse rate Γ (see dry adiabatic lapse rate ) yields
Γ = g/Cp=9,8°C/Km
where g denotes the earth's gravitational acceleration and Cp the specific heat at constant pressure
That means that the so-called "green house effect“ is just a misinterpretation of a well known physical correlation!
5. Contradiction to the second law of Thermodynamics
(see second law of Thermodynamics)
This law states that heat always flows spontaneously from hotter to colder bodies, and never the reverse, unless external work is performed on the system.
Everybody knows that principle: An oven heats up a room by burning fuel, as long as the oven is warmer than the room.
The reverse was never observed. Nobody has ever observed that an oven has become warmer without burning fuel, just by cooling down the room beneath.
Just a heat pump can pump heat from a lower temperature level to a higher temperature level, but to this end energy is necessary.

One can compare that heat flow with a ball which can roll only downhill by itself but not uphill!
But just that impossibility is claimed by the "green house effect“: higher and therefore cooler layers of air should heat up lower and therefore warmer layers of air!
This impossibility is explained by reflection of the heat by so called „greenhouse gasses“, which in reality nobody understands.
Obviously an analogy is insinuated to the capability of clouds to reflect heat. A cloud of water vapour represents a atmospheric boundary layer which is indeed able to reflect heat.
If CO2 would occur concentrated in clouds, it would also be able to reflect heat.
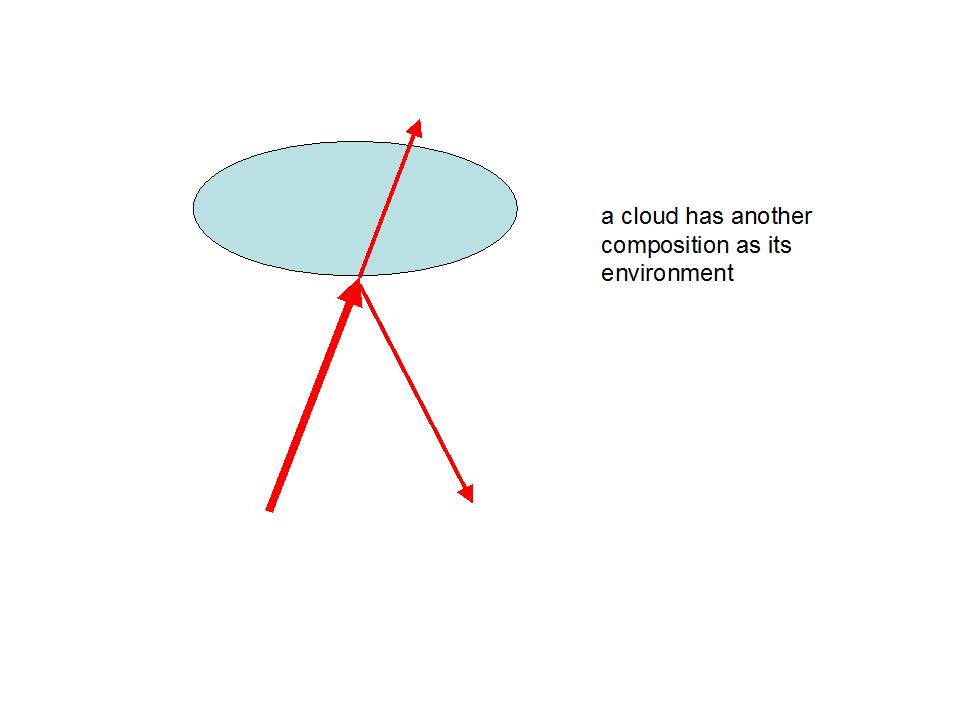
Within a homogenous and isotropic media in which no direction is preferential, no reflection can occur in any direction! Therefore "greenhouse molecules“ cannot reflect on average heat to the ground.
Each direction in the space is equivalent.
Possible are only scattering effects, which do not prefer any direction like the Rayleigh scattering yielding the blue color of the sky.
In reality the atmosphere is not isotropic and homogenous because its density declines with the height.
According to the "greenhouse effect“ the higher layers of thinner air should reflect heat into the lower layers of thicker air. Obviously only the reverse is possible:
only the lower layers of thicker air can reflect heat into higher layers of thin air (similar as a cloud) according to the second law of thermodynamics!
6. Interaction radiation and "greenhouse-molecules"
The claim that so-called "greenhouse gasses“ can reflect heat is based on a lack of understanding how heat radiation and molecules can interact. This interaction shall be explained as follows.
Let us consider a CO2 molecule. This molecule has an elongated shape. It chemical bond arises from the fact that both the oxygen atoms remove two electrons from the carbon atom building a stable second outer shell of 8 electrons.
No electrons remain in the second outer shell of the carbon atom. For the carbon atom only two electrons in the first shell remain.
Therefore both the oxygen molecules are twofold negatively charged and the carbon molecule is fourfold positively charged.
This yields to a powerful attraction between the atoms.
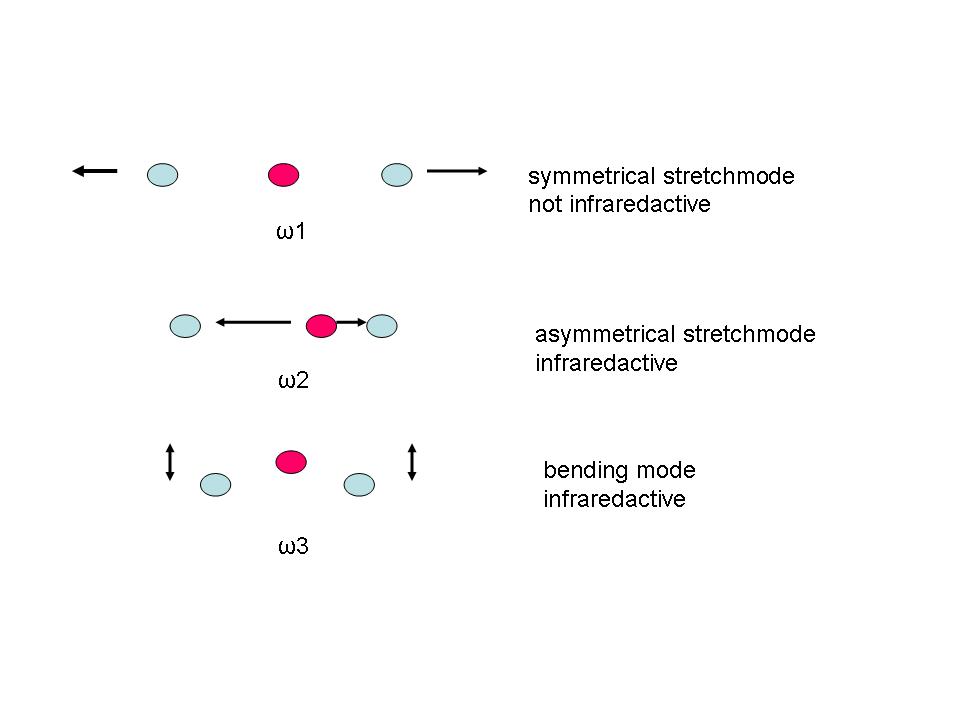
An electrical three-pole arises. Therefore electromagnetic waves of appropriate frequencies can stimulate the CO2 molecule to vibrate. A CO2 molecule can vibrate with only three distinct vibrational modes:
Symmetric stretch mode, anti symmetric stretch mode and bending mode (see Natural Frequency).
The most simple oscillator is the pendulum, which can only oscillate with a single frequency. According to this principle pendulum clocks have been built for centuries.
Another example is a quartz crystal for clocks and computers.
The stimulation of the vibration can only be done by the eigenfrequency. One can try it with a pendulum:
as long as the stimulation occurs with the eigenfrequency of the pendulum the amplitude of the oscillation becomes greater and greater (resonance).
If the stimulation occurs with a different frequency, the oscillation of the pendulum will be hindered and in the end stopped.
A molecule vibration can according to the above-described principle only be stimulated by an electromagnetic wave with the appropriate eigenfrequency.
This stimulation can only occur if the vibration is connected with a change of the charge distribution of the molecule.
In case of the CO2 molecule this is not the case for the symmetric stretch mode. Therefore this mode is called infrared-inactive,
because it cannot be stimulated with a infrared wave, or thermal radiation even with the appropriate frequency.
Infrared active are therefore, as far as the CO2 molecule is concerned, only the asymmetric stretch mode and the bending mode.
If a vibration is stimulated, energy is absorbed from the radiation field (absorption).
Eventually this vibration is annihilated and the appropriate infrared wave will be re-emitted.
In the meantime the molecule performs all kind of movements, especially rotations. Therefore it cannot be predicted in which direction the re-emitted wave proceeds.
After a short distance that re-emitted wave will be again absorbed by another CO2 molecule and after a while re-emitted, and so on.
After each absorption and re-emission the wave will move in any other direction.
Because the density of CO2 molecules decreases with increasing altitudes, the probabilty of an up-moving wave to be absorbed is smaller as the probability of a down-moving wave.
Therefore the waves absorbed by CO2 molecules will tend to move upward in accordance with the second law of thermodynamics.
The above described procedure is more or less hypothetical to proof that the radiation absorbed by CO2 molecules has to move upward and not downward.
In reality another process is more dominant:
Each air molecule collides permanently with another air molecule. So do also the CO2 molecules.
Molecule vibrations can therefore be stimulated with the support of these collisions (see remark below).
That means that vibrations can also be stimulated with some probability with radiation frequencies which slightly deviate from the eigenfrequency.
Therefore a small frequency band occurs around the eigenfrequency, which can stimulate a specific vibration.
However this process acts also the other way round: the molecule vibration can be annihilated by a collision and the vibrational energy will be transformed into
kinetic energy of the whole molecule corresponding to frequencies untypical to CO2.
This process lead in fact to a lack of CO2 specific frequency bands in the radiation of the earth into the universe.
Eventually this lack is often assumed as a proof for the "reflection“ of CO2 related radiation, but in reality, the corresponding energy is only distributed to other frequencies.
Any reflection of infrared radiation by CO2 molecules contradicts both the fundamental law of thermodynamics and the radiation law which all are well proofen laws and can also not be realized
if interaction between radiation and molecules are considered.
As opposed to those well-proofen laws there exists not one single proof of a greenhouse effect of molecules like CO2 or others on a laboratory scale.
Only computer simulations are used to "proof“ this claimed "green house effect“, but those calculations deliver only those results which the programmers and his customer wants to get.
This has nothing to do with physics.
Remark: This collisions can also support the stimulation of vibration indirectly by stimulating rotations of the molecules. These rotations can also help to stimulate molecule vibrations.
7.Experimental disproof of the so called "green house effect"
The so called "green house effect" alledgedly caused by absorption of infrared radiation has been disproofed since 1909!
see Experiment on Greenhouse Effect
